Raj Bhandari (Industrial Business Unit Head, GlobalLogic) discusses the advantages and technologies of Industry 4.0, focusing on digital twin technology and how businesses can start implementing it.
Archives
In the highly competitive market of the OTT industry — where the big players like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Spotify are leading the race with a wide variety of content and immersive UI/UX experiences — setting oneself apart from other players requires an effort to understand the audience and truly cater to their needs and preferences.
The success of any OTT platform depends on these key factors: content, discovery, user interface, and user experience. Personalization — the ability to understand the audience and serve them relevant content — targets all these factors. Learn more about how to develop a successful personalization strategy for OTT and which tools and technologies to leverage for implementation.
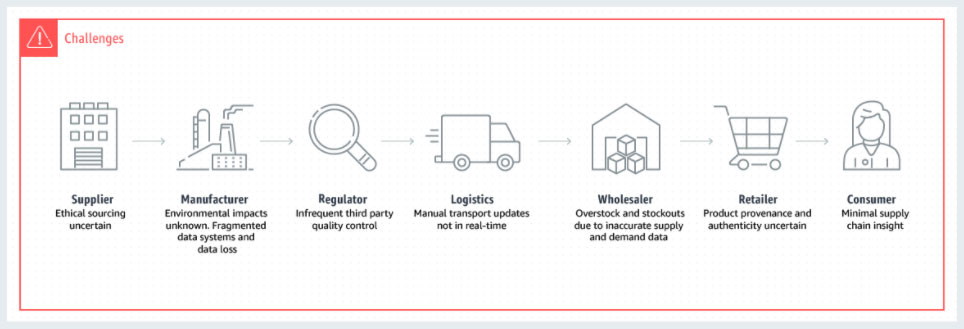
The use of blockchain has grown significantly since its original use as a form of cryptocurrency for ecommerce transactions. Businesses that rely on supply chains and smart contracts (e.g., manufacturers, distributors, suppliers, retailers, restaurants) are using blockchain (along with other technologies like cloud, analytics, AI/ML) to achieve their digital transformation / Industry 4.0 goals. This is especially true now during the recent pandemic, which has significantly disrupted supply chains across multiple industries. Let’s take a deeper look into how enterprise-level blockchain is helping businesses fix broken supply chains, accelerate recovery times, secure transactions, track product information, and reduce operating costs.
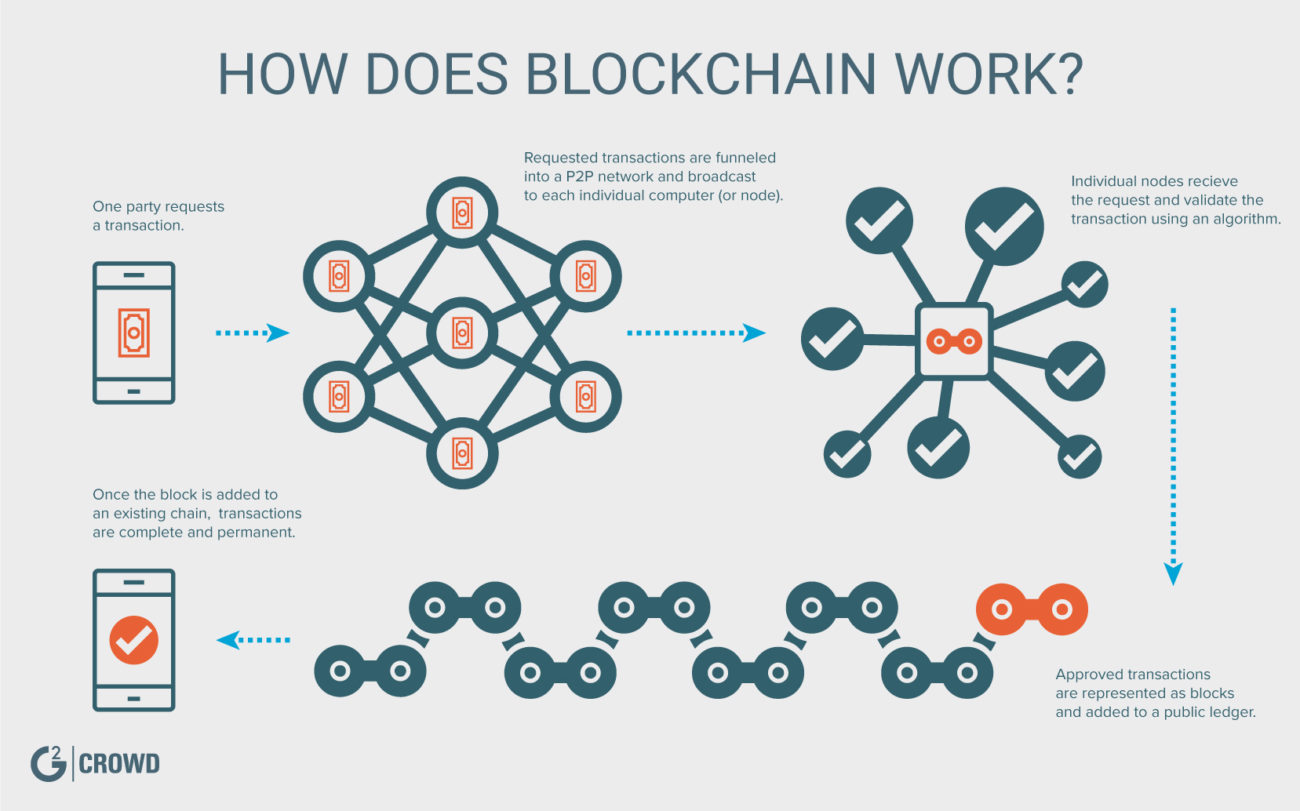
How Does Blockchain Work?
For those who are new to the term, blockchain is defined as a “distributed, decentralized, public ledger.” Put more simply, blockchain is a record-keeping technology. Each “block” is a piece of digital information (e.g., transaction data, participants, etc.) that is stored in a “chain” (i.e., a database that is distributed across a network of computers). When two or more parties engage in a smart contract or transaction through blockchain, each block of data is automatically verified and then made available to all parties to view for ultimate transparency.
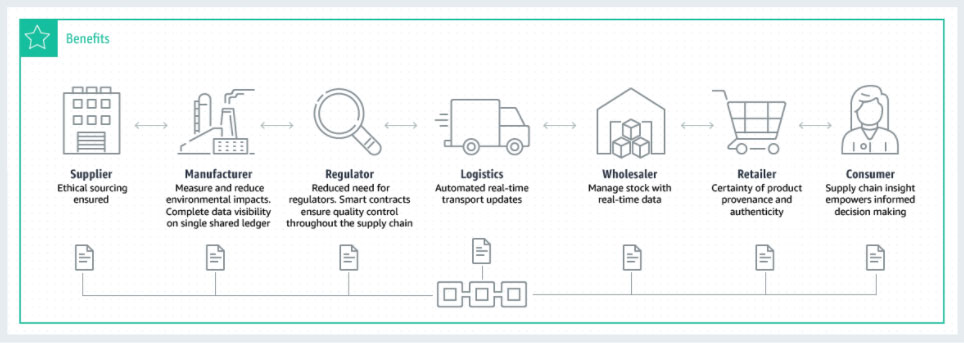
How Blockchain Impacts Supply Chains
Blockchain enables companies to create a decentralized environment through which they can streamline supply chains and securely engage in transactions of various kinds.
1) Data Security & Reliability
Since the blockchain network continuously and independently verifies the data of the transaction, all involved parties can be assured of the accuracy, reliability, and trustworthiness of the exchange. Neither party can falsify data, and because blockchain uses cryptography and security protocols to link themselves, no one can hack into or manipulate the data. Gartner predicted that companies using blockchain smart contracts will increase their overall data quality by 50% by 2023, and for supply chains.
2) Transparency & Traceability
Once the submitted data is verified through the chain, it is made available for all involved parties, ensuring that everyone is working with the same data and avoiding potential miscommunications. Transparency is especially important for supply chain management, as it allows businesses to record and view detailed information about each product, such as price, quality, current location, date of sale, certification, etc. This level of detail is crucial for preventing fraud, tracking products for recalls, predicting maintenance issues, and more. According to Deloitte, “The availability of this information within blockchain can increase traceability of material supply chain, lower losses from counterfeit and gray market, improve visibility and compliance over outsourced contract manufacturing, and potentially enhance an organization’s position as a leader in responsible manufacturing.”
3) Transaction Monitoring & Enforcement
Blockchain ensures that all transactions and agreements are followed to the letter. For example, once deployed, blockchain smart contracts are immutable and irrevocable through non-modifiable code, which enforces a binding commitment to do or not do something in the future. For businesses that create digital products, such as 3D designs, blockchain can help track products to enforce usage rights — ie, making sure that customers are not using the product beyond the terms of the purchase agreement.
4) Cost & Time Savings
Using blockchain enables businesses to bypass third party intermediaries and microservices (or, at the very minimum, make these engagements more efficient). By automating labor-intensive processes through blockchain and reducing their dependence on external parties like lawyers, bankers, shipping agents, etc., businesses accelerate timelines, eliminate expensive fees, and lower their risk of having their supply chain being disrupted. Blockchain can even help businesses quickly identify second sources if the supply chain is disrupted.
Traditional Supply Chains
Supply Chains with Blockchain
Case in Point
A recent example of using blockchain within the Industrial sector is logistics company Teleport, a division of AirAsia. Earlier this year, Teleport launched Freightchain, the world’s first digital air cargo network to run on blockchain. Freightchain assigns shippers and their freight forwarders to cargo connections to help them with their supply chain needs and facilitate bookings in real-time, which are processed on-chain and confirmed through a blockchain smart contract.
In a traditional system, a shipper must manually inquire about the availability of connecting flights with multiple airlines and agents. This oftens requires a lot of time spent on phone calls and emails. Freightchain simplifies the booking process and confirms itineraries 10 times faster by programmatically discovering the available routes with connecting flights within the shipper's budget and passing on significant cost savings to shippers.
Not only does blockchain enable Teleport to significantly accelerate its booking processes, but the dynamic on-demand interlining of flights also helps airlines improve otherwise underutilized flights.

Before You Get Started
It’s not easy, or advisable, to jump directly into creating an enterprise blockchain solution. Before you get started, here are 3 questions you should ask yourself:
1) What problems are you trying to solve with blockchain?
Is your main concern eliminating third-party intermediaries to save on costs? Are you trying to automate time-consuming manual processes? Do you need a smart solution that can help you identify new sources when parts of your supply chain get disrupted? By prioritizing the problem or problems you are trying to solve with blockchain, you can build out your business’s unique case and make better decisions about which kind of system to build, which technology to use, and how to implement it in the real world.
2) How will you design, build, and implement my blockchain system?
We recommend doing a small proof-of-concept (PoC) and tweaking your implementation based on the results. If replacing an existing system, consider running the blockchain alongside the legacy system. This way you can test and validate the new system with real data, but still use the legacy system to ensure continued production until you are ready to transition completely to blockchain. In addition, if you don’t have expertise in-house, we recommend working with a service provider who can get you started quickly.
3) Which technology is right for my business needs?
There are many, many blockchain technology options available in the market today — all with their own specific pros and cons, depending on your specific use case requirements (here is a comparison chart of popular enterprise blockchain technologies). One of the most common blockchain technologies available for the last few years is HyperLedger, an open source tool from the Linux Foundation that has multiple use cases and libraries available in the public domain. For those wanting to use blockchain for their supply chains, HyperLedger Grid provides data models, reference models, and smart contract-based business logic. Again, this is where a development partner with blockchain expertise is helpful.
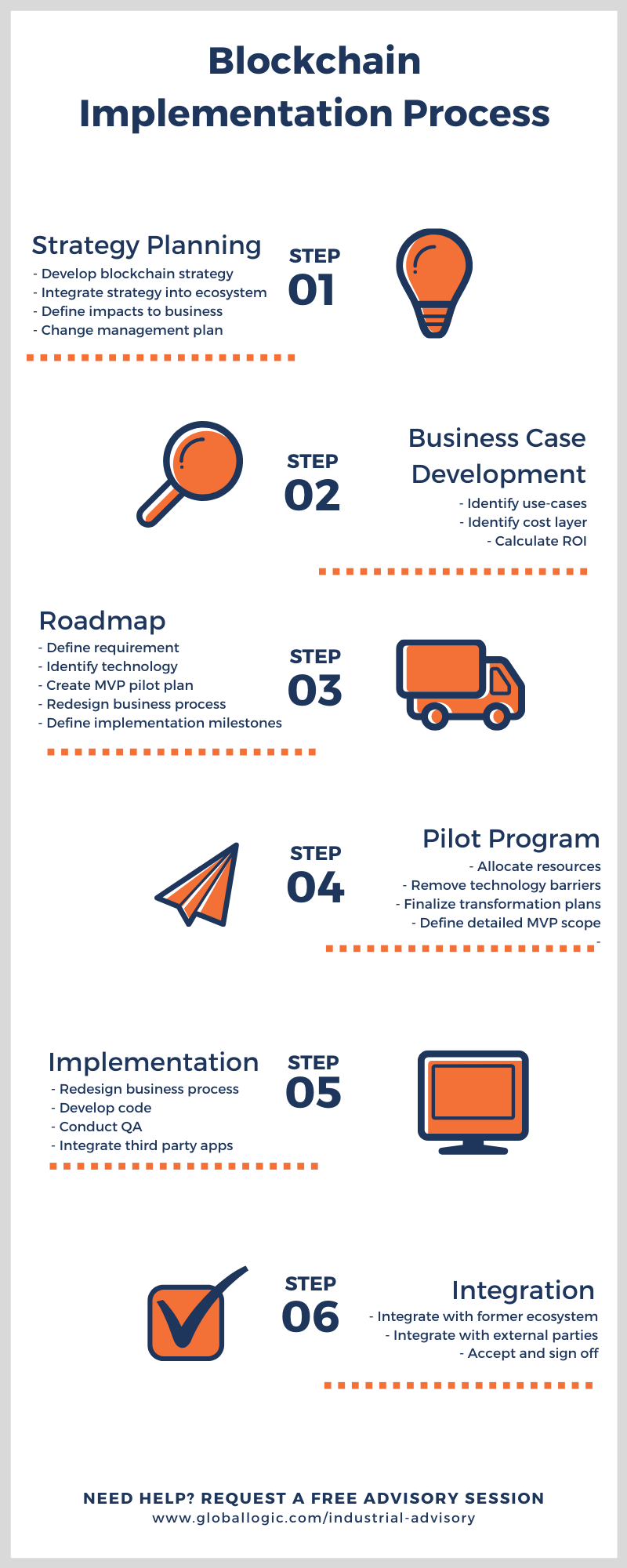
After you have educated yourself on blockchain (or engaged in an advisory session with a blockchain expert) and decided that it does in fact fit the bill, here’s a guide on how to implement it:
Conclusion
Blockchain is having a major impact on how businesses manage their supply chains and engage in transactions. By automating manual processes and creating a neutral, secure environment for processing data, businesses can trust that their data is safe, reliable, and accessible at all times. To learn more about how blockchain can help you further develop your digital transformation / Industry 4.0 roadmap, we suggest checking out the below resources.
Suggested Reading
Forbes | “Bringing Blockchain into Industry 4.0”
IBM | “What are Smart Contracts on Blockchain?”
Enterprise AI | “Blockchain: Streamlining Disrupted Supply Chains During COVID Crisis”
O’Reilly | Getting Started with Enterprise Blockchain
Gartner | Blockchain Platforms Market
What's Next in Digital Transformation?
Digital transformation is not new anymore. Organizations have been integrating digital technology to transform their different parts of the business. That fundamentally changes how you operate your business, serve your customers, and build a culture at your organization. Enterprises need to look beyond digital transformation to maintain a competitive advantage and stay relevant in their business. There is no question about undergoing digital transformation. All organizations must transform digitally, or else they will be pushed out of the business.
In the past 10 years, cloud, analytics, and digital experiences have been the focus of digital transformation, disrupting business models and markets. Although these technologies are still important, they are universal. Organizations need to look at the post-digital era to deliver a personalized and unique experience to their customers and employees. New technology trends are emerging that enable companies to deliver personalized experiences to customers. The power of Artificial Intelligence and cloud computing will continue to advance. Combining these technologies with ambient computing, blockchain, and extended reality will change the relationship of both an organization's customers and employees.
Let's take a look at the six technology trends that will dominate the digital transformation market for the next 5-7 years.
1. Personalization & Individualization
Personalization and individualization is about knowing your customers and providing them with a personal service. Current examples include inserting a customer's name in marketing emails, sending them coupons on their birthday or anniversary, etc.
The quantity of data that customers provide to companies has significantly increased in the past few years. Customers don't just want companies to remember their birthdays and send them coupons; they want businesses to predict what they want and when they want it. For example, retailers should be able to identify customers who have children and offer them specific offers for back-to-school, summer vacation, etc. Healthcare providers should tell patients when they may fall ill and how to prevent it. Streaming media services should be able to target ads and content to viewers with increasing accuracy.
Customers simply don’t have time to wade through data points and figure out what to do/buy/watch/etc. Instead, they are willing to share their data with companies in exchange for helping them make decisions. One-size-fits-all does not work anymore. Technology is here to provide customers an absolutely individualized experience that is tailored to their needs at that moment.
2. Ambient Computing & Presence
“Presence” will be the next buzz word in relation to IoT. Presence means having context awareness and knowing the surroundings of the customer. To provide a personalized experience to the customer, devices/platforms must understand their presence. For example, playing music or setting the thermostat should be personalized to the unique person in the room.
Voice assistants can now recognize the sound of a person's voice and behave differently to the same command from different people, but this is just the beginning. New possibilities will open up using computer vision, sensors, and voice interfaces to power ambient computing. Ambient computing allows people to use computers without realizing they are doing it. Ambient computing provides an experience using multichannel human-machine interfaces.
Over the past few years, tech companies have been pushing devices and sensors to every part of a person's life, from smart speakers in a vehicle to smart TVs in the living room — and even connected refrigerators. The primary goal of putting these devices in our lives is to understand our surroundings and respond to them. People do not even realize they are using computers to get things done. For example, the smart systems in your house can learn your wake-up time to adjust the thermostat, open your blinds, and tell the coffee machine to start brewing a hot coffee. As you enter the kitchen to get the coffee, your smart speaker can then start reading you the daily news. Ambient computing eliminates the friction between you and these computing devices.
3. Digital Trust
Gaining customers’ trust is not just important in products and services, but in the core purpose and principles to an organization's success. During the digital transformation journey, business leaders are asking customers to trust them with their personal information to track behavior and serve them better.
Organizations need to be transparent about the data they collect from customers and what they do with that data. Giving customers control over their data and providing them with tools to control the data they want to share will help to gain the customer’s trust, such as the way Amazon and Google give users an option to manage digital assistant activity. Companies should place AI-based automated checks to reduce fraud and suspicious account activities. The beyond-digital era will be built on trust, and organizations can not ignore it.
4. Digital Reality
Digital Reality means using the power of Augmented Really, Virtual Reality, or Mixed Reality to deliver meaningful, immersive experiences. Organizations are exploring extended/digital reality to both enhance the customer experience and improve employee productivity. Imagine that an elevator technician can open their smartphone, get insights from a faulty circuit board, and then communicate with an expert sitting remotely to fix the problem together.
Digital reality is already transforming education, automotive, healthcare, and retail. For example, NASA's conceptual "Eyes of Exoplanets" project and the Lunar and Planetary Institute both enable visitors to explore planets new and old through a 3D smartphone app. Nike uses AR App to help you find the right fit for your sneakers. Projects like these open new possibilities and business models for companies, and a new way to engage with customers.
5. Intelligent Interfaces
We are moving beyond click, type, touch, and swipes to more natural and personal interfaces using voice, gestures, and emotions. Voice devices like Amazon Alexa and Google Home are providing a natural way to interact with technology and get things done. It is so natural that both a 3-year-old child or 90-year-old grandfather can naturally interact with it. Voice interfaces are not just limited to speakers; they are embedded into kitchen appliances, cars, doorbells, and much more.
Sensors can detect our emotions and provide personal responses at any moment. Intelligent interfaces will be connected to each other to provide an individualized and context aware experience. Voice assistants can now differentiate between voices and provide the right information to the person who asked it. For example, “What’s on my calendar today?” will give different results for different people in the house.
6. Everything AI/ML
Enterprises are testing the waters by applying Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning to specific use cases and business functions. They have started gaining valuable insights that drive them to think about how machines and humans interact together. These enterprises are in a position to predict and automate actions based on these decisions. For example, Google’s Duplex AI project is an assistant that can make phone calls on our behalf to book appointments at restaurants or hospitals. This AI assistant is so intelligent and natural that it can interact with humans on the other side to book an appointment.
This is just the beginning of AI/ML; it is going to transform every touchpoint of the customer experience and business processes. Over the next 5–10 years, every problem will become an AI problem. Augmented Intelligence is the next step beyond Artificial Intelligence, where humans and machines work side-by-side. For example, Walmart is using robots to perform inventory checks. Sephora uses AR and digital displays in their stores to help customers try out products virtually, and to help store associates better recommend products to customers.
Conclusion
Digital transformation has enabled companies to serve digital customers, and now they need to continue on this path for the beyond-digital phase to meet the ever-increasing demands and expectations of customers. The beyond-digital era will use emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Machine Reality (MR), and Internet of Things (IoT) to shape the future of all industries over the next 5–10 years. This is the time to start working on these emerging technologies, to drive new innovations, and to transform new business models from the ground up.
Many of us are “digital citizens”; we are used to living in a technical world. Some of us were born into it, others migrated to it and became “naturalized,” and a few are still around who helped create that world in the first place.
To us, living online is an everyday thing, and has been for a long time. Video conferences, “drop boxes,” live chats, and many other forms of digital communication are everyday, normal things for us. Even before the crisis, we shopped online, got our entertainment online, connected online — and we are therefore very much at home with the digital aspects of the current environment.
While we “citizens” certainly miss our daily contact with actual fellow humans, alternate means of connecting are second nature to us. While not as satisfying, perhaps, they are also not in themselves a major challenge for us to use and cope with.
This is not the case for a large number of people, some of them our own loved ones. Some people are being forced by the COVID-19 crisis to connect in ways they never have before. For them, this is its own source of stress. These are the “digital refugees” who find themselves driven to our native or adopted “digital country” as a result of the COVID-19 crisis.
I have several of these “refugees” in my own family, and I bet you do too. Like many Silicon Valley couples, I am a “techy” married to a “non-techy." My wife is, in fact, a clinical psychologist who—while certainly not tech-averse—is also not a digital citizen. She has found herself having to meet clients and staff using—to her—unfamiliar video conferencing tools. While she has been pleasantly surprised to find that therapy can still be very effective in this way, the tools themselves drive her crazy. As a fellow shut-in due to shelter-in-place orders, I’ve found myself in the tech support role at very frequent intervals. I’ll bet that most of us “citizens” also find ourselves giving aid to the “refugees” in our circle.
My 89-year-old father is also a very surprising refugee in our digital world. My siblings and I have been trying for years to get him connected to the internet, but he has been resistant. This is despite the fact that when you google my name (“James F Walsh,” same as his) my father’s memoirs about the Korean War in the Library of Congress are page-ranked much higher than anything I’ve ever written.
As another couple sheltering in place (he and my Mom still live independently), my Dad was cut off from his sole connection to the Internet—the public library. Persuaded by my daughter, his granddaughter, he finally agreed to try. I sent my Dad my last-generation iPad and—to my surprise and delight—he loves it. He has been FaceTiming the whole family, accessing the internet, responding to email—and generally taking to the digital age like a duck to water. I was thrilled to see this refugee to our land—at 89 years old—look like he wants to stay.
I in no way want to minimize the plight of physical refugees who are fleeing from oppression, warfare or starvation and trying to find a better life. In fact a member of my own family experienced this early in the 20th Century. However I am struck by the parallels of the current situation to the physical one.
Forced to retreat by this disease from many forms of engagement with the “physical” world, we have fled to a digital one. While many of us are at home there, others most definitely are not. We who are at home find ourselves in a position where we must help these refugees live in our world. Some of those refugees will like this new land and want to stay; others will “go home” as soon as they can. And all of us, refugee and citizen alike, will be very much altered by this event—let’s hope, in some ways at least, for the better.
In this white paper, GlobalLogic’s Mobile Practices Team rates the various features of cross-platform mobile frameworks to help readers choose the best technology stack for developing or expanding a mobile application. We also provide recommendations on when to apply which technologies for different types of mobile applications.
Like all other companies across various industries, GlobalLogic is adapting to a new normal in the wake of COVID-19. As I write this, I am still “sheltering in place” in my home in California. Like previous crises, I expect that COVID-19 will expose many financial and other weaknesses that already existed. Unlike other crises, though, the novel coronavirus crisis is uniquely—or perhaps we should say “cruelly”—suited to exposing companies who have not pivoted strongly to digital.
In this crisis, literally hundreds of millions of people have been forced by the pandemic to stay at home, for weeks and months at a time. Companies whose products and services are exclusively provided through physical channels—brick-and-mortar retail, restaurants, travel, personal care services like barbers and hairdressers, as well as many others—are being severely impacted.
While some businesses can never be entirely digitized, those that can (or have quickly figured out how) to provide products and services through digital channels have fared better. Digital pioneers like Amazon and Facebook are seeing enormous surges in demand, and restaurants that have been able to support food orders or even grocery items through the Web are far more likely to survive than those who have not.
Walmart has certainly benefited from the fact that their grocery sales allow their physical stores to stay open while many other brick-and-mortar retailers were forced to shutter. However, the retailer’s investment in digital technology to manage inventory, warehousing, and logistics are clearly key enablers to help cope with the fantastic up-tick in demand.
Even those businesses who already have a successful digital engagement strategy often have another digitally-related challenge: to scale fast enough. As people migrate their meetings and other forms of social engagement online, those conferencing and collaboration services that are able to scale with the huge surge in volume are the ones that are succeeding.
GlobalLogic traditionally used whatever video conferencing system our clients chose, so I’m familiar with them all. However, recently we’ve all found out first-hand that only a small number of these services work well in the face of the huge levels of demand they are now experiencing. Not surprisingly, the one that seems to be standing up the best (rhymes with “Loom”) claims that they use a cloud-first distributed architecture. In other words, they are the video conferencing solution that appears to be a “digital native.”
What is the lesson? In addition to the financial and other impacts of past crises, the COVID-19 pandemic also uniquely exposes weaknesses in a company’s digital transformation efforts. The ability to offer goods and services through digital channels is key to survival—while the ability to scale seamlessly to meet demand is equally necessary to prosper. These facts were true even before the pandemic, but this crisis has made it undeniably clear how much the world has changed. People now “live” online as much (or more than) they live in a physical space; this is true of your customers and of your employees.
The more your systems, business models, and products are aligned to this new reality, the better your company is probably coping with this crisis—at least relative to your competitors in the same industry. And even when we’ve beaten this scourge, having a digitally transformed company will make your business better suited to meet the reality of a changing world.
In the meantime—stay safe and stay well!
Surveys show that 70-80% of home Wi-Fi users experience issues, from low Wi-Fi performance to no connectivity to Wi-Fi Access Points. GlobalLogic offers Internet Service Providers (ISPs) with a comprehensive solution that can be deployed at any customer location to monitor the area’s Wi-Fi environment, predict the customer’s Wi-Fi quality of experience, and even take certain actions to improve it. Check out the below explainer video to learn more:
Mocking is a process that is used in unit testing when the unit being tested has external dependencies. For example, a code that initiates the downloading of an image (and finally conveys success-failure on the UI) will have a dependency on a NetworkModule. While unit testing this code, the NetworkModule should be mocked. The purpose of mocking is to isolate and focus on the code being tested and not on the behavior or state of external dependencies. So in simple words, mocking is creating objects that simulate the behavior of real objects.
In Android, there are a lot of frameworks used for mocking in unit testing, such as PowerMock, Mockito, EasyMock, etc. MockK is definitely a better alternative to other mocking frameworks for Kotlin, the official development language for Android. Its main philosophy is first-class support for Kotlin features.
Mockito Framework and its Shortcomings
I started off with adding the Mockito dependency to my Kotlin project and wrote a simple unit test case.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<version>2.13.0</version>
</dependency>
class DatabaseTest {
class GenerateRecord { fun generate(): String = "Random String" }
class Dao { fun insert(record: String) = println("""Inserting "$record"""") }
class Service(private val generator: GenerateRecord, private val dao: Dao) {
fun calculate() {
val record = generator.generate()
dao.insert(record)
}
}
val generator = Mockito.mock(GenerateRecord::class.java)
val dao = Mockito.mock(Dao::class.java)
val service = Service(generator, dao)
@Test
fun insertRecordTest() {
val mockedRecord = "mocked String"
Mockito.`when`(generator.generate()).thenReturn(mockedRecord)
service.calculate()
Mockito.verify(generator).generate()
Mockito.verify(dao).insert(mockedRecord)
Mockito.verifyNoMoreInteractions(generator, dao)
}
}
When you ran it, It gives you this nice error:
org.mockito.exceptions.base.MockitoException:
Cannot mock/spy class GenerateRecord
Mockito cannot mock/spy because :
- final class
— anonymous classes
— primitive types
As all classes and methods are final by default in Kotlin, using Mockito appears to be a bit problematic due to how Mockito creates its mocks. You would have to explicitly make your classes inheritable using the open modifier. Another approach would be to add interfaces to everything.
Starting from Mockito version 2.0.0, it did become possible to mock final classes (although it is an incubating, opt-in feature). This, however, requires a bit of a setup really.
The Idiomatic Mocking Framework for Kotlin
MockK’s main philosophy is offering first-class support for Kotlin features and being able to write idiomatic Kotlin code when using it. Adding MockK is as simple as ever; you only have to add the dependency to your project, and you are set to go.
testCompile "io.mockk:mockk:${mockkVersion}"
class DatabaseTest {
class GenerateRecord { fun generate(): String = "Random String" }
class Dao { fun insert(record: String) = println("""Inserting "$record"""") }
class Service(private val generator: GenerateRecord, private val dao: Dao) {
fun calculate() {
val record = generator.generate()
dao.insert(record)
}
}
val generator = mockk<GenerateRecord>()
val dao = mockk<Dao>()
val service = Service(generator, dao)
@Test
fun insertRecordTest() {
val mockedRecord = "mocked String"
every { generator.generate() } returns mockedRecord
every { dao.insert(mockedRecord) } just Runs
service.calculate()
verifyAll {
generator.generate()
dao.insert(mockedRecord)
}
}
}
Now it is time to talk about such features as captured arguments and mocking.
Syntax In Mockk
First, you need to create a mock:
val mock = mockk<Type>()Then, you can stub some calls with argument matchers or regular arguments:
every {mock.call(any(), any())} returns 5Stubbed mocks can now be used in some tested code and called as regular objects.
mock.call(2, 3) // returns 5After testing is done, you can verify calls again with matchers or regular arguments:
verify {mock.call(2, 3)}That's it for the basics, but there is a lot more. Check out the documentation and examples here.
Capturing
Argument capturing can make your life easier if you need to get a value of an argument in every block or verify a block. Let’s say that we have the following class:
There are two ways to capture arguments: using CapturingSlot<Int> and using MutableList<Int>.
CapturingSlot allows you to capture only one value, so it is simpler to use.
val slot = slot<Int>()
val slot1 = slot<Int>()
val mock = mockk<Addition>()
every { mock.call(capture(slot), capture(slot1)) } returns 5This creates a slot and a mock. You can set expected behavior following way: in case mock.call is called, then arguments are captured to the slot and 5 is returned.
Now for the code being tested:
mock.call(2, 3) // 5 is a resultAfter executing it, the slot.captured value is equal to the first argument (i.e. 2).
Now you can do some checks. Assert for example:
assertEquals(2, slot.captured)That is basically it. Working with MutableList is the same, but instead of using a slot in the capture function, MutableList should be used.
val list = mutableList<Int>()
val mock = mockk<Type>()
every { mock.call(capture(list), any()) } returns 5Conclusion
Mockito felt a bit too Java-ish when using it in a Kotlin project. MockK, being a newer library specifically targeted at Kotlin, felt clean and pleasant to use with excellent documentation.
In celebration of International Women's Day 2020, we're proud to highlight one of our own premier women in tech, Sunny Azadeh. As GlobalLogic's Chief Information Officer, Sunny has over 20 years of IT and business experience—as well as a strong reputation for building innovation and driving change.
What does it mean to be a CIO?
A CIO's mission is to be a trusted and transparent partner as we help build out business processes and platforms for growth, compliance, and employee delight. My goal is to connect people and processes through technology, identify future opportunities to evolve GlobalLogic's enterprise architecture, and mentor and develop leaders within my team.
Have you always wanted to work in tech?
I fell in love with computer programming during my very first class at San Jose State University. I enjoyed the challenge of working through logical processes to solve different problems. I saw technology as an art form, so I immediately changed my major to computer science engineering. In fact, I was one of the few females to attend the computer science department at SJSU when it was first established.
What has your journey to CIO been like?
I am what you call an "accidental CIO." I started my journey as employee #1 in a startup as a software engineer. I then transitioned to a larger company as a software engineer, and during the economic downturn I transferred to IT at the same company—not even knowing what IT meant! During the many years of my career progression, I found that what made me the happiest in my career was the opportunity to innovate and transform, and to see the impact and value it delivered to the business. I exited my second company as CIO (one of the few female CIOs in the Valley at the time), and since then I have had several roles as sitting CIO. I also started up my own software company and two consulting companies.
What has been the most fulfilling part of your career?
The people who mentored and sponsored me in my own career were amazing, which is why building up the next generation of IT leaders is so important to me. I'm proud to say that three of my "mentees" have successful consulting companies, and another three are sitting CIOs themselves. I also helped develop a Directors Group as part of my membership with the Consortium of Information System Executives. This group has successfully helped members navigate the path to CIO for nearly 20 years now. Mentorship and community engagement are most fulfilling for me.
What motivates you to work in tech, and what do you think is the “next big thing?”
I love to build and learn, and I get to do both in my role—from developing people, to developing myself, all the way to developing applications and infrastructure. I believe the next big thing is the intersection of many technologies coming together, powered by connectivity over the 5G network. Connected anything via Artificial Intelligence is also on the horizon. However, I am worried that we lack the privacy, security, and rules of engagement for this next phase in technology.
What do you think needs to change to bring more women into the tech industry?
There is a lot of focus on gender, but I believe the focus should be on diversity, which includes many other aspects. That said, we need to create an opportunity early on in our education system for all students to explore computer sciences, and to empower our youth with choices. I am delighted to see so many efforts in this space today, from Girls who Code to AnnieCannons, a not-for-profit focused on transforming survivors of human trafficking and gender-based violence into software engineers and entrepreneurs.
The second stage of getting more women into technology is ensuring equality in pay and career opportunities. There has been some progress made over the past 10 years, and there is a lot more good work to be done in this space. I encourage all leaders to step up and help; it requires a shift in mindset to purposefully build diverse teams.
What advice would you give to women who want to pursue a career in tech?
One word: grit. Be passionate and persistent in following your dreams. Ask for help, find mentors and sponsors, ask for what you need, and build the path for both yourself and the next generation to follow. If tech is what you love, then tech is what you can do. Drive a career that is aligned with your passion, map out what you want to do, and be flexible to pivot as needed.