- Services
Technology Capabilities
Technology Capabilities- Product Strategy & Experience DesignDefine software-driven value chains, create purposeful interactions, and develop new segments and offerings
- Digital Business TransformationAdvance your digital transformation journey.
- Intelligence EngineeringCreate high-value products faster with AI-powered and human-driven
- Software Product EngineeringCreate high-value products faster with AI-powered and human-driven engineering.
- Technology ModernizationTackle technology modernization with approaches that reduce risk and maximize impact.
- Embedded Engineering & IT/OT TransformationDevelop embedded software and hardware. Build IoT and IT/OT solutions.
- Industries
- GlobalLogic VelocityAI
- Insights
White PapersSeptember 17, 2024Diana SocaciuElevating Romanian Tourism with GlobalLogic: Apuseni App
The innovative banking apps, such as the one we'll explore in this case study, succeed ...
 Case StudiesGlobalLogic
Case StudiesGlobalLogicFrom Legacy to Leading-edge: A Global Software Leader’s ...
Discover how GlobalLogic’s AI-powered solutions helped a global software leader migrate...

- About
Published on June 14, 2023Remote Health Monitoring Benefits, Challenges & Solutions
View all articles Abhishek GedamPrincipal Architect,TechnologyShare
Abhishek GedamPrincipal Architect,TechnologyShareLet's start engineering impact together
GlobalLogic provides unique experience and expertise at the intersection of data, design, and engineering.
Get in touchCloud Platforms - HyperscalersData EngineeringEnd-to-End IoT SolutionsHealthcare and Life SciencesPre-pandemic, “remote health monitoring” was not a common term in the average person’s lexicon. Major technology and healthcare companies have heavily invested in research and launching various health monitoring sensors and related ecosystems, and today, remote health monitoring is gaining acceptance and adoption among the general public.In the post-pandemic world, personal health care is an increasing focus and priority. The major benefit of remote health monitoring is obvious: caregivers may need to avoid physical meetings with patients but still need an ecosystem where all vital data is available remotely to aid in diagnosis and treatment.
Aside from infectious disease concerns, patients suffering from chronic illnesses require ongoing monitoring of vital parameters. Clinicians can reduce barriers to access for patients when daily/routine health monitoring and consultation can be done remotely, with physical meetings limited to major intervention and diagnosis. The benefits of remote health monitoring are many, and technology has a critical role to play.
We’ll explore remote health monitoring advantages, use cases, and solutions, but first – an important point of clarification. Remote health monitoring refers to the collection of patient vitals, while “remote clinical consultation” focuses on remote treatment and doctors’ recommendations based on vitals and other available patient data. We’ll focus on remote health monitoring in this article.
Types of Health Monitoring
Monitoring patient vitals such as body temperature, pulse, oxygen saturation, weight, and other factors inform medical consultations and are an important part of the diagnosis of symptoms. Regular monitoring becomes even more important for patients undergoing treatment and suffering from disease.
Traditionally, vitals monitoring has been done at the hospital or clinic where the patient is being treated. However, this has evolved with increasing technological innovation and the falling costs of monitoring devices/sensors. Three major classifications of health monitoring today include:
-
- In-person monitoring: The patient and clinician must physically meet in order to perform vitals monitoring.
- On-demand monitoring: The patient or their caregiver can monitor their vitals at home as scheduled.
- Implicit monitoring: Smart, wearable devices implicitly collect and monitor vital patient data.
How Remote Health Monitoring Helps
Remote health monitoring combines on-demand and implicit monitoring, helping doctors and other healthcare practitioners gain ongoing visibility of patient data that can signal changes in the patient’s health condition. This is crucial for patients suffering from diseases. In some cases of typical disease, patients seem on the road to recovery during hospitalization but see their health problems return within a few weeks of discharge. Remote Health Monitoring can help in such cases to provide post-discharge monitoring.
One solution is to have a full-time trained nurse to track patient vitals. However, this is expensive and not sustainable, making it impractical to serve every patient like this.
Remote health monitoring platforms offer an alternative via a set of medical devices and sensors connected to a mobile application and/or a suite of remote applications to monitor and relay patient data to clinicians. This provides healthcare providers with an ongoing view into patient health so that they can monitor an existing treatment plan or intervene based on inputs from medical devices and health sensors.
Recommended reading: Digital Biomarkers: The New Era of Wearable Technology
Remote Health Monitoring Advantages
Remote health monitoring is a boon to patients with chronic illnesses who require close attention to body vitals. Other major advantages of the technology include:
- Overall improvement in post-hospitalization value-based care.
- Close engagement with patient chronic illness by monitoring patient health remotely.
- A reduced number of hospital visits reduces barriers for patients with mobility issues.
- Reduced number of readmissions in hospital.
- Helps in social distancing.
- Helps in addressing the shortage of trained health professionals.
- Regular health monitoring of patients can aid in earlier disease detection and better treatment outcomes.
Remote Health Monitoring Challenges
As with other remote monitoring solutions (such as predictive maintenance in manufacturing), remote health monitoring relies on connectivity to ensure data syncing between sensors and the devices clinicians use to access those insights. Other major challenges include:
- Latency in data syncing.
- Onboarding and patient learning to wear and maintain the new device.
- Data inconsistency and duplication.
- Remote configuration of devices and debugging.
- Data ingestion from devices with different output formats.
Remote Health Monitoring Device Classifications
Medical devices and sensors to measure body vitals are the most important part of a remote health monitoring solution. While most devices are external, modern technological advances mean some of these devices can be embedded and serve multiple purposes. For example, some pacemakers can control heartbeat while also tracking and delivering vital information about heart condition.
There are limitations; for example, devices and sensors preprogrammed to take readings at a particular event or time must sync with mobile applications over Bluetooth. Some devices must be operated manually to take required vitals readings, with data entered manually into an application. With that in mind, we can broadly group medical devices and sensors into the classifications below.
Implicit Reading Devices
These devices collect vitals data without manual intervention and can include:
- Implantable or embedded devices that serve a specific purpose, such as cochlear implants or pacemakers.
- Wearable devices such as a smartwatch or pedometer.
Manual Reading Devices
The patient or their caregiver is required to take the reading and input data. One example of such an external device is a pulse oximeter.
Remote Health Monitoring Use Cases
There are many possible workflows for remote health monitoring. Mapping out the workflow is an important part of solution design and enables all stakeholders to see how and where patient data is being used, and what decisions are being made based on it.
Here, we examine a common workflow for a patient discharged from the hospital and in need of ongoing care:
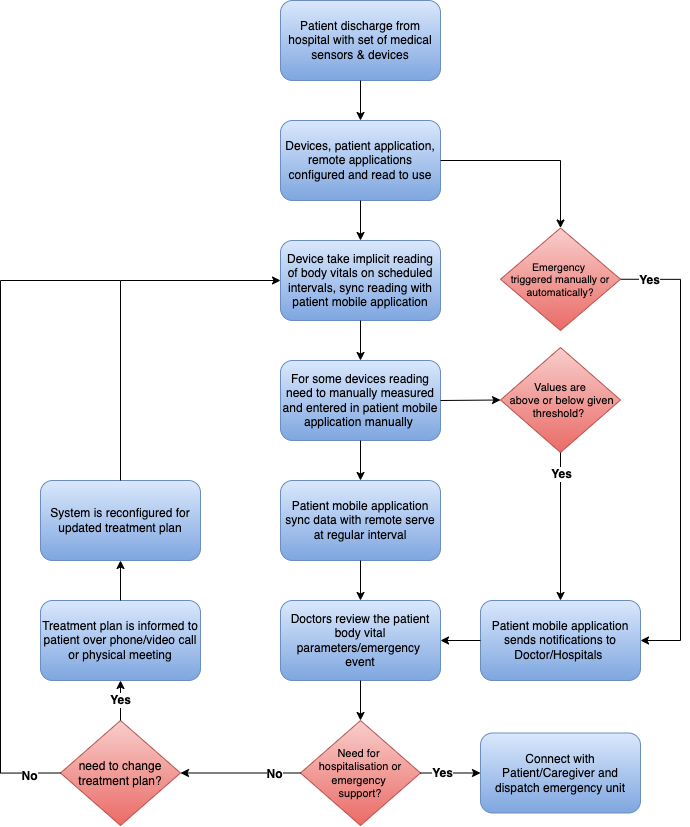 There are many use cases already in practice today, and innovations in the space are opening up new opportunities for remote health monitoring each day. Here are several more ways this technology can be used to benefit patients and improve healthcare outcomes.
There are many use cases already in practice today, and innovations in the space are opening up new opportunities for remote health monitoring each day. Here are several more ways this technology can be used to benefit patients and improve healthcare outcomes.Workplace safety and injury prevention
In many industries, shifts are long and tiring, and lapses in judgment or human error can lead to major financial losses and even loss of life. In aviation, heavy machinery operation, natural resource extraction, and even healthcare itself, the stakes are high. Remote health monitoring solutions can provide a system of wellness checks for professionals involved in high-risk workplaces.
Insurance
Technological advancements are enabling insurance companies to use data from remote health monitoring services to decide on yearly premiums. Individuals with healthy records can be awarded a reduced premium as compared to individuals with risk factors identified in the collected data.
Athletes
Vitals data can contain significant insights for athletes and sports personalities, with body parameters differing for each athletic and sporting activity. For example, a javelin thrower may want to measure the speed of their run to give optimum results. A swimmer might benefit from blood oxygen insights to help improve performance. Health monitoring can be modified with a new set of sensors and devices to create solutions for various types of athletes.
Fitness enthusiasts
Individuals increasingly want to live a healthy lifestyle, and monitoring body parameters can help. There are already various solutions available, such as wearable fitness devices. The engagement of fitness enthusiasts can be further increased by modifying remote health monitoring solutions to track and evaluate other aspects of daily life such as sleep quality, or screen time.
Important Considerations for Evaluating RHM Solutions
The specific qualities and capabilities of your solution will depend largely on the needs of your business, patients, and healthcare professionals. In a broad sense, quality remote health monitoring solutions will have most or all of the following characteristics:
- Simple device onboarding and registration with patients as well as hospitals.
- Frequent collection of data from devices and synchronization with remote services with minimum latency.
- Business rules optimized to raise alarm warnings and emergency notifications.
- Fulfillment of emergency notifications.
- Unified communication solutions to provide end-to-end communication.
- Scheduling for patient and doctor/hospital physical or virtual meetings.
- Interoperability solutions for smooth flow of patient records.
- Billing and subscriptions.
- HIPAA compliance to safeguard PHI.
 Example: The IoMT FHIR Connector for Azure
Example: The IoMT FHIR Connector for AzureRemote health monitoring platforms face common core challenges, including data ingestion at high frequency, scalability to add new devices, and data interoperability.
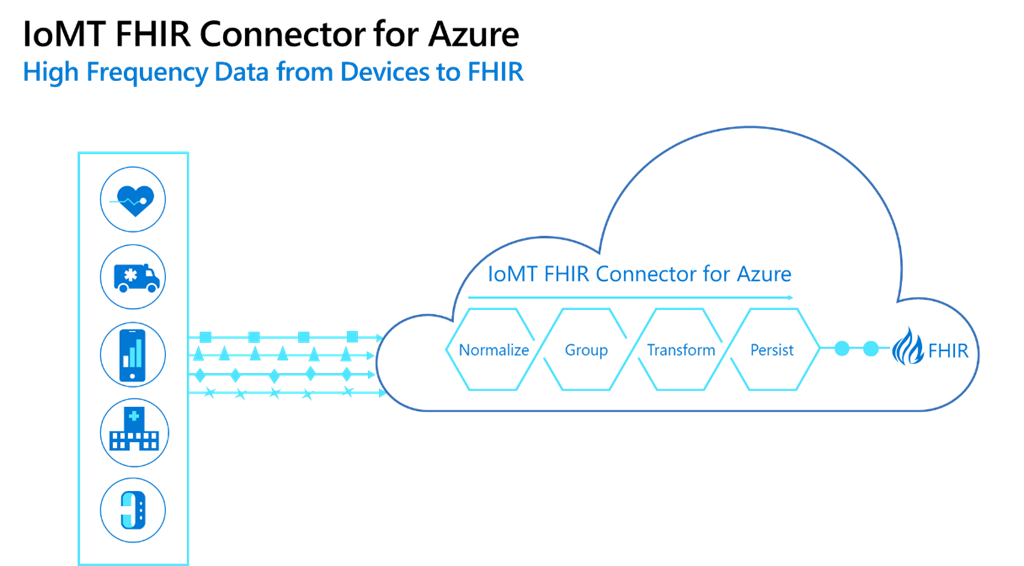
The IoMT FHIR Connector for Azure tried to solve all these problems by providing tools for seamless data-pulling from medical devices (IOMT). Data is pushed securely to Azure for remote health monitoring. In this way, this solution also solves problems around lack of interoperability by persisting data in a FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) server. Learn more in the github repository.
Conclusion
Remote health monitoring is a rapidly evolving space, with much research ongoing and new solutions being released regularly. Though there are many off-the-shelf solutions available, solutions can be built from the ground up – or around open-source tools like IoMT Connector for Azure – to meet the specific needs of patients and their healthcare providers.
Want to learn more? Explore how we’re revolutionizing healthcare experiences with technology here, or reach out to a member of the GlobalLogic team with questions.
Learn more:


