- Services
Technology Capabilities
Technology Capabilities- Product Strategy & Experience DesignDefine software-driven value chains, create purposeful interactions, and develop new segments and offerings
- Digital Business TransformationAdvance your digital transformation journey.
- Intelligence EngineeringLeverage data and AI to transform products, operations, and outcomes.
- Software Product EngineeringCreate high-value products faster with AI-powered and human-driven engineering.
- Technology ModernizationTackle technology modernization with approaches that reduce risk and maximize impact.
- Embedded Engineering & IT/OT TransformationDevelop embedded software and hardware. Build IoT and IT/OT solutions.
- Industries
- GlobalLogic VelocityAI
- Insights
BlogsNovember 6, 2023GlobalLogicOntology – key Enabler of Next-Gen Technologies
Every big or mid-sized company has a proliferation of sites, edge devices, apps, and di...
 BlogsNovember 30, 2023GlobalLogic
BlogsNovember 30, 2023GlobalLogicSmartphone on Wheels
Over the past decade, cars have undergone a significant transformation to provide a mor...

- About
Published on January 25, 2023Deploying a Landing Zone with AWS Control Tower – Part 2
View all articles Adam DivallSolutions ArchitectShareRelated Insights
Adam DivallSolutions ArchitectShareRelated Insights Richard Lett5 March 2025
Richard Lett5 March 2025 Yuriy Yuzifovich4 March 2025View All Insights
Yuriy Yuzifovich4 March 2025View All Insights GlobalLogic26 February 2025
GlobalLogic26 February 2025Let's start engineering impact together
GlobalLogic provides unique experience and expertise at the intersection of data, design, and engineering.
Get in touchAnalyticsData EngineeringCross-IndustryPreviously in Part 1, we delivered a brief background on what a Landing Zone is, before going through how to launch AWS Control Tower as the foundation of a Multi-Account Architecture.Part 2 of the blog series will walkthrough some of the initial post configuration activities with Control Tower, including setting up the organisational structure and enabling guardrails.
What has Control Tower deployed?
As part of the setup, Control Tower has utilised a number of other AWS Services including:
- AWS CloudFormation: This has been utilised for provisioning resources through Infrastructure as Code (IaC) across the multiple AWS Accounts, using a combination of both Stacks and StackSets.
- AWS CloudTrail: An Organisational Trail has been configured in the Management AWS Account. This Trail is configured to: monitor all AWS regions, send its logs to an S3 Bucket (that is in the Log Archive account), is encrypted using the KMS CMK that was created during the Control Tower setup, has Log File Validation Enabled, is integrated with CloudWatch Logs and also configured to send notifications to an SNS Topic in the Audit Account when new logs files are sent to the S3 Bucket.
- Amazon CloudWatch: CloudWatch Log Groups are created as part of the integration with the CloudTrail Trail, as well as any execution of the Lambda Functions deployed by the Control Tower setup.
- AWS Config: An Organisation Config Aggregator is created within the Management Account and Config Recorders are created in all AWS Accounts within the AWS Organisation, except for the Management Account. In addition, several Config Rules will be created as part of the Mandatory Guardrails configured during the setup process.
Quick note: Since Control Tower doesn’t create a Config Recorder in the Management Account, AWS Config is something that should have been enabled in all AWS Accounts. We will explain how you can do this using Customisations for Control Tower later in the blog,
- Amazon EventBridge: An EventBridge Rule is created within all AWS Accounts except for the Management Account to trigger a Lambda Function on any Config Rule Compliance Change.
- AWS IAM: Several IAM Roles are created including IAM Service Roles. The IAM Roles have IAM Permissions Policies added to them to grant the relevant level of permissions, and the Trust Policies are configured to allow the Role Assumption by only specific Source AWS Accounts, AWS Services or via the SSO Identity Provider using SAML.
- AWS IAM Identity Centre: This service gets enabled within the Home Region of Control Tower to provide Single Sign-On. Several Groups & Permission Sets are created, and those Groups then have a Permission Set assigned to them against the provisioned AWS Accounts within the AWS Organisation (Management, Audit and Log Archive Accounts). A User is also created that maps to the e-mail address of the root user of the Management AWS Account.
- AWS KMS: AWS Managed KMS keys are utilised for the encryption of data at rest in conjunction with the creation of the S3 Buckets. In addition, as part of our setup configuration we also created a Customer Managed Key (CMK) to encrypt the CloudTrail Trail.
- AWS Lambda: A Lambda Function is created within all AWS Accounts except for the Management Account. This Function is used as part of the mechanism for forwarding notifications of Config Rule compliance changes.
- AWS Organisations: This has been used to create the Organisation which is crucial to a multi-account setup. As part of the Organisation, it has then setup two Organisational Units (OU) that were defined during the Shared Accounts page of the Control Tower setup. Typically, these OUs will be named Security (in previous versions of the Control Tower service it was named Core) and the other Sandbox. In addition, several Service Control Policies (SCP) will have been created as part of the Mandatory Guardrails configured during the setup process.
- Amazon S3: Two S3 Buckets are deployed within the Log Archive account.
- One Bucket is used for the storage of CloudTrail and Config logs as part of a Centralised Logging Solution. It is configured with Default Encryption using KMS (AWS Managed Keys), has Versioning enabled, a Bucket Policy to restrict access, is configured to Block Public Access, Access Logging enabled and is configured with a Lifecycle Policy.
- The second Bucket is used for the storage of the S3 Access Logs. It is configured with Default Encryption using KMS (AWS Managed Keys), has Versioning enabled, a Bucket Policy to restrict access, is configured to Block Public Access, Access Logging enabled and is configured with a Lifecycle Policy.
- AWS Service Catalog: A Portfolio is created with a Product added that provides Control Tower with Account Factory component.
- Amazon SNS: An SNS Topic is created within all AWS Accounts except for the Management Account. That Topic has a destination of a Lambda Function that forwards the message to another SNS Topic in the Audit Account, which in turn sends an e-mail to the e-mail address assigned to the root user of the Audit Account.
- AWS Step Functions: Whilst the Control Tower setup implements State Machines that is used as part of the wider orchestration and for the Account Factory element, these are not visible within any of the AWS Accounts that exist in the AWS Organisation. These are under the control and management of AWS as part of the Service Offering.
Organisational Structure
When considering organisational structure, there is a really good blog post from AWS on the Best Practices for Organisational Units (OU) that describes each of the OUs and their purpose. Please note, these are just guidelines and should be tailored to meet the needs of your particular business.
The diagram below is based on what can typically be seen when working with Clients. We’ve also outlined steps to creating the OU structure.
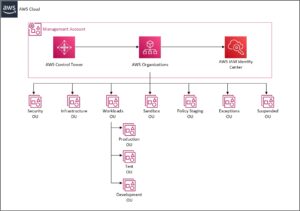
Creating the Organisational Units Structure
- Login to the AWS Management Console and Navigate to Control Tower.
- Click Organisation.
- Click Create resources and then select Create organisational unit.
- On the Add an OU page; enter the OU Name, click Parent OU and then select the OU Name to replicate the high level organisation layout.
Once configured it will look something like the below screenshot.
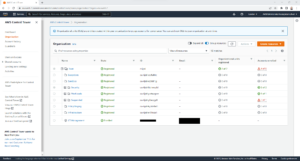
Please note: Only Organisation Units that have been created through the Control Tower Console will show a state of “Registered” on the Organisation page in Control Tower. If the Organisation Unit was created either via the AWS CLI or within AWS Organisations, it will show a state of “Unregistered” and will therefore need to be registered by selecting the OU in question on the Organisation page in the Control Tower console, selecting “Actions” and then clicking “Register organisational unit”.
Once you’ve created your OU Structure, you’re ready to configure guardrails.
Configuring Guardrails in Control Tower
Guardrails are rules that enable you to provide ongoing governance and oversight across your environment. In terms of guardrails within Control Tower there are two different types – preventative and detective.
Preventative guardrails are implemented through Service Control Policies (SCP) and stop you from going outside of a specific set of boundaries, as defined within the SCP. Since SCPs are implemented at the Organisation level, it provides a layer of control over all AWS Accounts within the organisation without needing to implement something directly in every single AWS Account.
Detective guardrails are implemented through Config Rules and will send notifications if a resource within the individual AWS Account doesn’t adhere to the settings within the rule. For example, if the rule says that all EBS Volumes must be encrypted and there is an EBS Volume within the Account that isn’t, it will notify you.
Control Tower guardrails can only be implemented on Organisation Units and not directly on AWS Accounts. That’s not to say you couldn’t create something customised but in that case, you would need to write some automation to do this and it wouldn’t be shown within the Control Tower console, if something was non-compliant.
Enabling a guardrail in Control Tower creates a CloudFormation StackSet in the Management Account. Leveraging the integration with AWS Organisations adds a CloudFormation Stack Instance for each AWS Account, residing within the hierarchy of the OU that the guardrail was enabled onto the StackSet. This in turn creates a CloudFormation Stack within the corresponding AWS Account. Similarly with the disabling of a guardrail, it deletes the Stack Instance from the StackSet and then deletes the Stack from the corresponding AWS Account.
How to enable and disable a guardrail
We’ve covered what happens when you enable a guardrail. Now let’s walk through how you go about enabling and disabling a guardrail from scratch. Both processes are similar, but obviously you will need to have enabled a guardrail before being able to disable it!
- Login to the AWS Management Console and Navigate to Control Tower.
- Click ‘Guardrails’.
- Find the guardrail that you want to implement by either scrolling through the pages until you locate it or by using the filter mechanism.
- Click the Name of the guardrail. For example, “Detect whether public read access to Amazon S3 buckets is allowed”.
If the guardrail is already enabled and you’re looking to disable, click the ‘Disable guardrail’ option – like so:
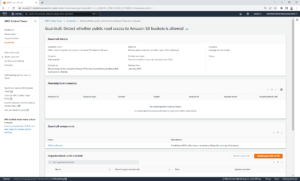
If you’re looking to enable a guardrail for the first time, click on the ‘Enable guardrail on OU’ button. The ‘Disable guardrail’ option should be greyed out.
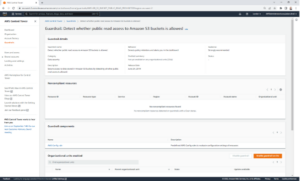
- A new page will load – click the ‘Enable guardrail on OU’ button again to enable.
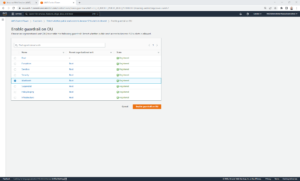
From here:
- Select the OU that you want to enable/disable the guardrail on and then click Enable guardrail on OU or Disable guardrail.
- Repeat the process again for each OU that you want to enable/disable the guardrail on. Unfortunately, at this moment in time, it can’t be added or removed from multiple OUs at the same time.
Repeat the process for all guardrails that you wish to enable.
And that’s it. You’re good to go.
Part 3 of this blog series will continue with the remaining post-deployment activities within Control Tower – including configuring IAM Identity Centre and provisioning a new AWS Account through Account Factory.
About the author:
Adam Divall, Solutions Architect at GlobalLogic with over 20 years demonstrable experience in design, implementation, migration and support of large, complex solutions to support a customer’s long term business strategy. Divall holds all 12 available certifications for Amazon Web Services with specialisations including Networking, Security, Database, Data Analytics and Machine Learning.
This doesn’t sound right. What are you trying to say?
